- Details
- Written by Ismael Jones
- Category: Technical Info
- Published: 17 July 2004
- Hits: 6593
Battery performance as a function of cycling
As part of ongoing research to find the most durable battery system, Cadex has performed life cycle tests on nickel-cadmium, nickel-metal-hydride and lithium-ion batteries. All tests were carried out on the Cadex 7000 Series battery analyzers in the test labs of Cadex, Vancouver, Canada. The batteries tested received an initial full-charge, and then underwent a regime of continued discharge/charge cycles. The internal resistance was measured with Cadex's OhmTest method, and the self-discharge was obtained from time-to-time by reading the capacity loss incurred during a 48-hour rest period. The test program involved 53 cell phone batteries, of which one per chemistry was chosen for the charts below.Nickel-cadmium
In terms of life cycling, standard nickel Cadmium is the most enduring battery. Figure 1 illustrates the capacity, internal resistance and self-discharge of a 7.2V, 900mA nickel-cadmium battery with standard cells. Due to time constraints, the test was terminated after 2300 cycles. The capacity remained steady, the internal resistance stayed flat at 75mW and the self-discharge was stable. This battery receives a grade 'A' for almost perfect performance. It should be noted that nickel-cadmium has a moderate energy density, requires periodic full discharges and contains toxic metals.
 |
Figure 1: Cycle performance of standard nickel-cadmium. 7.2V, 900mAh This battery deserves an 'A' for almost perfect performance in terms of stable capacity, internal resistance and self-discharge over many cycles. |
 |
Figure 2: Cycle performance of ultra-high nickel-cadmium. 6V, 700mAhThis battery offers higher energy density than the standard version at the expense of reduced cycle life. |
Nickel-metal-hydride
Figure 3 examines nickel-metal-hydride. We observe good performance at first but past 300-cycles, the readings starts to deteriorate rapidly. One can observe the swift increase in internal resistance and self-discharge after cycle count 700. nickel-metal hydride has a higher energy density than nickel-cadmium and does not contain toxic metals. Some argue that nickel-metal-hydride is an interim step to lithium-ion.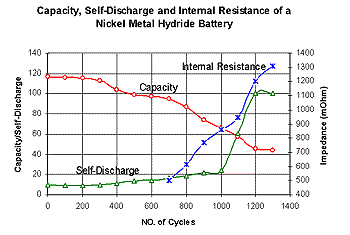 |
Figure 3: Cycle performance of nickel-metal-hydride 6V, 950mAh.This battery offers good performance at first but past 300 cycles, the capacity, internal resistance and self-discharge start to deteriorate rapidly. |
Lithium-ion
In Figure 4 we examine the capacity and internal resistance of a lithium-ion battery. A gentle and predictable capacity drop is observed over 1000 cycles and the internal resistance increases only slightly. Because of low readings, self-discharge has been omitted on this test. lithium-ion offers the highest energy density of the above-mentioned chemistries and contains no toxic metals. Limited discharge current, the need for safety circuits and aging are negative attributes of this battery. |
Figure 4: Cycle performance of lithium-ion. 3.6V, 500mAlithium-ion offers good capacity and steady internal resistance over 1000 cycles. Self-discharge was omitted because of low readings. |
Under a full cycle program, as conducted in this test, nickel-based batteries are not affected by crystalline formation (memory). Memory shortens battery life in everyday use if not properly maintained. Applying a full discharge/charge cycle once a month solves this problem. nickel-cadmium is more prone to memory than nickel-metal-hydride.
lithium-ion benefits from a controlled life cycle test because the aspect of aging plays a less significant role. The service life of lithium-ion in real life is a combination of cycle count and aging. All batteries are affected by aging in various degrees.
Another reason why life cycling produces positive readings is the controlled temperature environment in which the tests are carried out. In true life, the batteries meet much harsher treatment and are often exposed to heat. Furthermore, the batteries in our test were charged with a well-defined charge algorithm. Overcharge was minimized and damaging heat buildup prevented. Low-cost consumer chargers do not always service the battery optimally.
The type of load with which the batteries are discharged also plays a role. The above test consisted of an even DC discharge. Digital equipment load the battery with heavy current bursts. Tests have shown reduced cycle life when a battery is discharged with sharp current pulses as opposed to DC, even though the delivered end-energy is the same. Cell phones, laptop computers digital cameras are devices that draw heavy current spikes.
In some other aspects, however, a lab test may be harder on the battery than actual field use. In our test, each cycle applied a full discharge. The nickel-based packs were drained to 1.0 volt and lithium-ion to 3.0 volts per cell. In typical field use, the discharge before re-charge is normally shallower. A partial discharge puts less strain on the battery, which benefits lithium-ion and to some extent also nickel-metal-hydride. nickel-cadmium is least affected by delivering full cycles. Manufacturers normally specify the cycle life of lithium-ion at an 80% depth-of-discharge.










